Smart meter is an advanced energy meter that measures consumption of electrical energy providing additional information compared to a conventional energy meter. Integration of smart meters into electricity
grid involves implementation of a variety of techniques and software, depending on the features that the situation demands. Design of a smart meter depends on the requirements of the utility company as well as the customer. In fact, deployment of smart meters needs proper selection and implementation of a communication network satisfying the security standards of smart grid communication.
Image blow shows metering architecture of conventional and smart meter system.
Communication technologies to be chosen have to be cost efficient, should provide good transmittable range, better security features, bandwidth, power quality and with least possible number of repetitions. Bluetooth technology can be a possible option for communication of control signals and to transmit energy consumption
data. In the view of implementing this technique, Koay et al. proposed a Bluetooth based energy meter that can collect and transmit the energy consumption data wirelessly to a central base station. Power Line Carrier (PLC) and Broadband Power Line (BPL) communications are the other possible options of data transfer supporting the higher level communication suites such as TCP/IP. One of the popular communication technologies is PLC, which uses the existing electricity grid, cellular/pager network, mesh network, combination of licensed and unlicensed radio, wireless modem, existing internet connection, power line communication, RS-232/485, Wi-Fi, WiMAX, and Ethernet with protocol to upload data using IEC DNP. PLC technology is highly efficient for automation of data in smart meter applications. In spite of substantial overhead caused by the large IPv6 header, this protocol can be applied even at low PHY layer data rates. This technology, with the combination of the MAC algorithm can achieve satisfactory delay times and throughput. Though this combination might slightly reduce the usable data transfer rate, it will not affect the overhead at MAC layer. IP based network protocol would be another promising option for communication because of its advantages over other technologies while satisfying the security standards of the smart grid communications. In addition, TCP/IP technology can also be used as a common platform for multiple
communication devices.
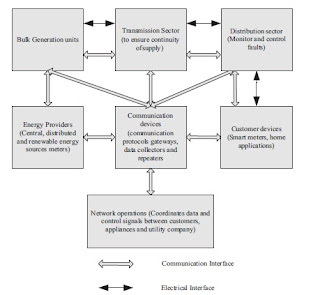
Figure below shows communication network for smart meter:
References:
1. Smart meters for power grid: Challenges, issues, advantages and status (Review Article) Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, Volume 15, Issue 6, August 2011, Pages 2736-2742 Soma Shekara Sreenadh Reddy Depuru, Lingfeng Wang, Vijay Devabhaktuni
2. Koay BS, Cheah SS, Sng YH, Chong PHJ, Shum P, Tong YC, et al. Design and implementation of bluetooth energy meter. In: Proc. Fourth International Conference on Information, Communications & Signal Processing. 2003. p. 1474–7.


No comments:
Post a Comment