-->
-->
LCD display is an inevitable part in almost all embedded applications and this article is about interfacing 16×2 LCD with 8051 Microcontroller. Many guys find it hard to interface LCD module with the 8051 but the fact is that if you learn it properly, it’s a very easy job and by knowing it you can easily design embedded display applications. Thoroughly going through this article will make you able to display any text (including the extended characters) on any part of the 16×2 display screen. In order to understand the interfacing first you have to know about the LCD.
What is 16×2 LCD Module?
16×2 LCD module is a very common type of LCD module that is used in 8051 based embedded applications. It consists of 16 rows and 2 columns of 5×7 or 5×8 LCD dot matrices. The module were are talking about here is type number JHD 162A which is a very popular one. It is available in a 16 pin package with back light, contrast adjustment function and each dot matrix has 5×8 dot resolution. The pin numbers, their name and corresponding functions are shown in the table below.
Pin No. Name Function
- Vss This pin must be connected to the ground
- VCC Positive supply voltage pin (+5V DC)
- VEE Contrast adjustment
- RS Register selection
- R/W Read or write
- E Enable
- DB0 Data
- DB1 Data
- DB2 Data
- DB3 Data
- DB4 Data
- DB5 Data
- DB6 Data
- DB7 Data
- LED+ Back light LED+
- LED- Back light LED-
VEE pin is meant for adjusting the contrast of the LCD display and the contrast can be adjusted by varying the voltage at this pin. This is done by connecting one end of a POT to the Vcc (5V), other end to the Ground and connecting the center terminal (wiper) of the POT to the VEE pin. See the circuit diagram for better understanding.
The JHD 162A has two built in registers namely data register and command register. Data register is for placing the data to be displayed, and the command register is to place the commands. The 16×2 LCD module has a set of commands each meant for doing a particular job with the display. We will discuss in detail about the commands later. High logic at the RS pin will select the data register and Low logic at the RS pin will select the command register. If we make the RS pin high and the put a data in the 8 bit data line (DB0 to DB7), the LCD module will recognize it as a data to be displayed. If we make RS pin low and put a data on the data line, the module will recognize it as a command.
R/W pin is meant for selecting between read and write modes. High level at this pin enables read mode and low level at this pin enables write mode.
E pin is for enabling the module. A high to low transition at this pin will enable the module.
DB0 to DB7 are the data pins. The data to be displayed and the command instructions are placed on these pins.
LED+ is the anode of the back light LED and this pin must be connected to Vcc through a suitable series current limiting resistor. LED- is the cathode of the back light LED and this pin must be connected to ground.
What is 16×2 LCD Commands?
16×2 LCD module has a set of preset command instructions. Each command will make the module to do a particular task. The commonly used commands and their function are given in the table below.
LCD Command Function
0F LCD ON, Cursor ON, Cursor blinking ON
01 Clear screen
2 Return home
4 Decrement cursor
06 Increment cursor
E Display ON, Cursor ON
80 Force cursor to the beginning of 1st line
C0 Force cursor to the beginning of 2nd line
38 Use 2 lines and 5×7 matrix
83 Cursor line 1 position 3
3C Activate second line
0C3 Jump to second line, position3
OC1 Jump to second line, position1
LCD initialization
The steps that have to be done for initializing the LCD display is given below and these steps are common for almost all applications.
- Send 38H to the 8 bit data line for initialization
- Send 0FH for making LCD ON, cursor ON and cursor blinking ON.
- Send 06H for incrementing cursor position.
- Send 01H for clearing the display and return the cursor.
Sending data to the LCD
The step for sending data to the LCD module is given below. I have already said that the LCD module has pins namely RS, R/W and E. It is the logic state of these pins that make the module to determine whether a given data input is a command or data to be displayed.
- Make R/W low.
- Make RS=0 if data byte is a command and make RS=1 if the data byte is a data to be displayed.
- Place data byte on the data register.
- Pulse E from high to low.
- Repeat above steps for sending another data.
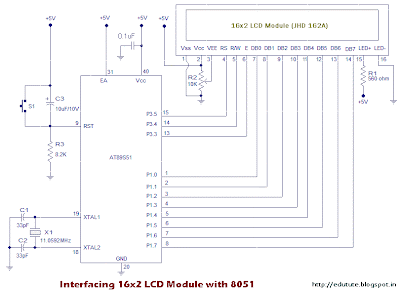
Circuit
The circuit diagram given above shows how to interface a 16×2 LCD module with AT89S1 microcontroller. Capacitor C3, resistor R3 and push button switch S1 forms the reset circuitry. Ceramic capacitors C1, C2 and crystal X1 is related to the clock circuitry which produces the system clock frequency. P1.0 to P1.7 pins of the microcontroller is connected to the DB0 to DB7 pins of the module respectively and through this route the data goes to the LCD module. P3.3, P3.4 and P3.5 are connected to the E, R/W, RS pins of the microcontroller and through this route the control signals are transferred to the LCD module. Resistor R1 limits the current through the back light LED and so do the back light intensity. POT R2 is used for adjusting the contrast of the display.
Assembly Program
MOV A,#38H // Use 2 lines and 5x7 matrix
ACALL CMND
MOV A,#0FH // LCD ON, cursor ON, cursor blinking ON
ACALL CMND
MOV A,#01H //Clear screen
ACALL CMND
MOV A,#06H //Increment cursor
ACALL CMND
MOV A,#82H //Cursor line one , position 2
ACALL CMND
MOV A,#3CH //Activate second line
ACALL CMND
MOV A,#49D
ACALL DISP
MOV A,#54D
ACALL DISP
MOV A,#88D
ACALL DISP
MOV A,#50D
ACALL DISP
MOV A,#32D
ACALL DISP
MOV A,#76D
ACALL DISP
MOV A,#67D
ACALL DISP
MOV A,#68D
ACALL DISP
MOV A,#0C1H //Jump to second line, position 1
ACALL CMND
MOV A,#67D
ACALL DISP
MOV A,#73D
ACALL DISP
MOV A,#82D
ACALL DISP
MOV A,#67D
ACALL DISP
MOV A,#85D
ACALL DISP
MOV A,#73D
ACALL DISP
MOV A,#84D
ACALL DISP
MOV A,#83D
ACALL DISP
MOV A,#84D
ACALL DISP
MOV A,#79D
ACALL DISP
MOV A,#68D
ACALL DISP
MOV A,#65D
ACALL DISP
MOV A,#89D
ACALL DISP
HERE: SJMP HERE
CMND: MOV P1, A
CLR P3.5
CLR P3.4
SETB P3.3
CLR P3.3
ACALL DELY
RET;
DISP: MOV P1, A
SETB P3.5
CLR P3.4
SETB P3.3
CLR P3.3
ACALL DELY
RET;
DELY: CLR P3.3
CLR P3.5
SETB P3.4
MOV P1, #0FFh
SETB P3.3
MOV A, P1
JB ACC.7, DELY
CLR P3.3
CLR P3.4
RET;
END
Subroutine CMND sets the logic of the RS, R/W, E pins of the LCD module so that the module recognizes the input data (given to DB0 to DB7) as a command.
Subroutine DISP sets the logic of the RS, R/W, E pins of the module so that the module recognizes the input data as a data to be displayed.

No comments:
Post a Comment